
Mature Markets Are Better Equipped to Keep Up with Demands for Ethical Compliance
While stakeholder interest and legislation push companies to greater environmental, social, and governance (ESG) due diligence, many overseas markets struggle to keep up with the demands for compliance. This puts companies at increased risk of compliance violations through their suppliers. This article provides insights on the regional disparities that influence the ability of suppliers to meet compliance standards.
The Importance of Supplier Compliance
Recent data from QIMA, drawn from a survey of over 800 businesses with international supply chains, underscores the increasing emphasis on ESG compliance. Nearly two-thirds of respondents from US- and EU-based businesses indicated that supplier compliance has grown in importance over the past year, largely due to a rise in ESG legislation and consumer expectations.
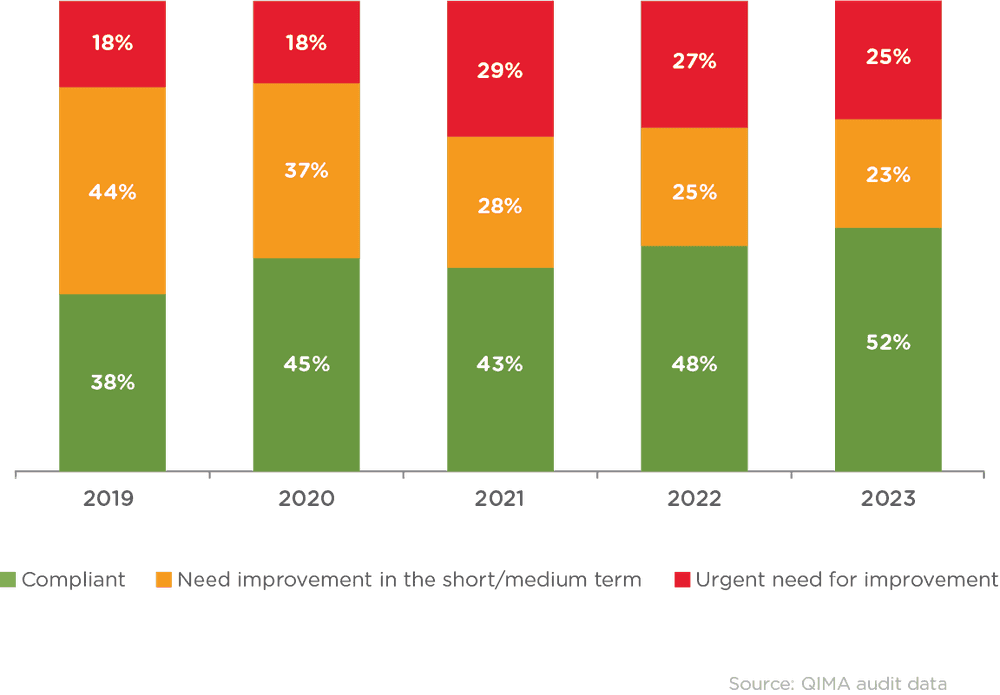
Although the demand for ethical sourcing in supply chains is growing, many overseas suppliers are struggling to keep up with compliance standards. Data from QIMA’s 2023 audits revealed that 25% of the inspected factories necessitated urgent remediation efforts.
Figure 1. Evolution of factory rankings assigned by ethical audits. Global averages of ethical audits revealing an urgent need for improvement have increased from 18% to 25% since 2019.
Supplier compliance violations of any degree put companies at risk of damaged brand reputation and supply chain disruptions. If a supplier’s operations are halted due to compliance violations – such as safety hazards, environmental degradation, or human rights concerns – buyers risk impacts to their production lines, or even face fines due to negligence.
Understanding how to select suppliers with low ESG compliance risk is a major step in ensuring your business operations run smoothly. Fortunately, QIMA data has revealed that regional variations are a key indicator of the ability of suppliers to uphold ESG standards.
Regional Disparities Impact Supplier ESG Compliance
Audit data from 2023 reveals a correlation between the maturity of a sourcing region and its ability to meet ethical compliance standards. In China, critical Health & Safety violations were recorded in 11% of audited factories. In stark contrast, India exhibited a much higher rate of violations at 29%. Such disparities highlight the struggles of developing nations in keeping pace with the stringent demands for ethical compliance imposed by international markets.
These trends are consistent across a wide variety of ESG factors, with immature markets like India experiencing critical violations at over twice the rate of more mature markets, including China and Vietnam. These violations often stem from a lack of resources that ensure safe infrastructure, equitable labor practices, and environmental consciousness.
Figure 2. Percentage of 2023 audits where critical violations were discovered. Audit data from 2023 shows India consistently receiving higher percentages of critical violations in ethical compliance categories, as compared to China- and Vietnam-based factories.
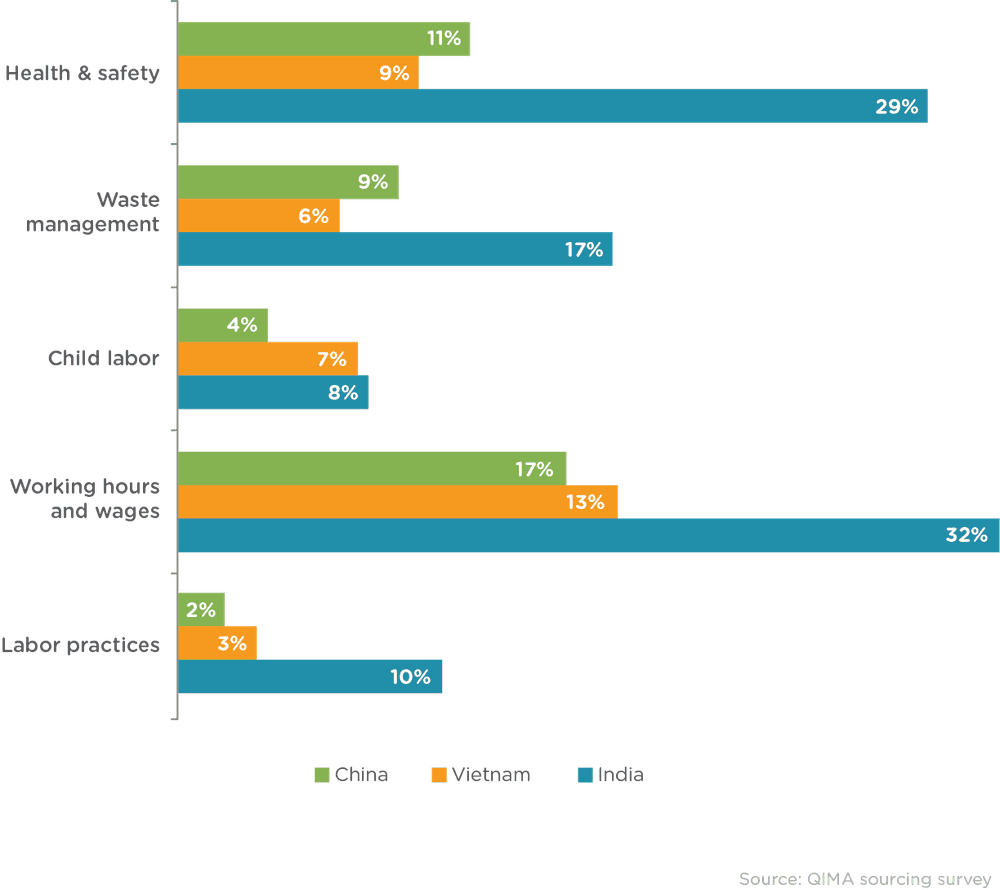
Key Figures
QIMA auditing data reveals:
Ethical compliance is on the rise: A growing percentage of global factories are compliant with ethical standards, with only 38% meeting compliance standards in 2019 and 52% meeting compliance standards in 2023.
A growing number of factories face an urgent need for improvement: Despite the rise in compliance, more factories are experiencing critical conditions, with 18% in 2019 and 25% in 2023.
Factories in India experience critical ethical violations: Auditing data revealed Indian factories received significantly more critical violations than those in Vietnam or China, particularly in the categories of Health and Safety and Working Hours and Wages.
Read the full report: Q1 2024 Barometer
Related Articles


