
Steps to Due Diligence Implementation: From Initial Assessment to Results
Embarking on the journey of implementing due diligence in your supply chain is a strategic move that demands precision and a comprehensive understanding of the steps involved.
In this article, we discuss the key steps of due diligence, ensuring a thorough exploration from the initial assessment phase to the tangible results that fortify the resilience of your supply chain.
What Is Supply Chain Due Diligence?
Supply chain due diligence refers to the systematic process of investigating, assessing, and managing potential risks and impacts associated with a company's supply chain activities. It involves the proactive identification, evaluation, and mitigation of social, environmental, and ethical concerns to ensure compliance with regulations, uphold responsible business practices, and enhance overall supply chain sustainability.
Most due diligence regulations are influenced by the OECD Due Diligence Guidance for Responsible Business Conduct, which covers human rights, employment and industrial relations, environment, and more.
Read more: What Is Supply Chain Due Diligence? A Guide to Navigating Ethical Manufacturing
Steps to Implementing Due Diligence
While a company must always check the specific requirements of due diligence legislation that applies to its business, operations, and supply chain, the OECD due diligence guidance outlines six basic steps for due diligence implementation. These steps represent a minimum of due diligence and serve as a foundational framework for supply chain managers looking to initiate the due diligence process.
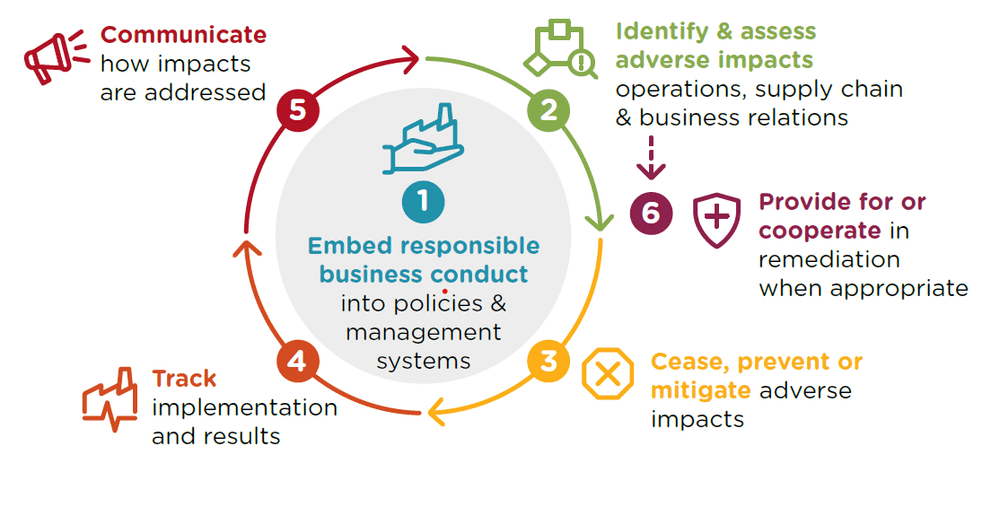
1. Embed responsible business conduct into policies and management systems
Step 1 involves the foundational process of embedding responsible business conduct into the very fabric of a company's policies and management. This starts with the development of explicit policies addressing responsible business conduct and due diligence, meticulously tailored to align with the company's operations, supply chain dynamics, and other business relationships. Crucially, these policies are not static documents but are actively woven into the decision-making processes, procedures, and training programs of the company, ensuring a seamless integration into daily practices.
Additionally, clear communication of these expectations extends beyond internal stakeholders, reaching out to business partners and suppliers. Collaborative partnerships are identified, fostering a collective commitment to responsible conduct and due diligence.
2. Identify and assess adverse impacts in operations, supply chains, and business relations
In this pivotal step, businesses undertake a comprehensive examination to identify and assess adverse impacts within their operations, supply chains, and business relations, laying the groundwork for informed decision-making and proactive risk mitigation. The activities listed below should be carried out and should involve relevant internal and external stakeholders.
Map the value chain, including direct and indirect suppliers and other business relations. Collect information on these parties:
What they do (business and sustainability)
Where they operate
How relevant they are for the business
What leverage exists
Perform a materiality assessment to understand the most salient issues. This should cover:
Impact of sustainability issues on the business
Impact of the business on sustainability issues
Develop and implement a risk assessment methodology and activities, including information for the above steps as well as inherent risk indicators (geography, sector, product) and information from early warning systems such as worker voice tools. Some due diligence legislations list industries that are viewed as higher risk.
Assess your business’s role in contributing to each impact, categorizing your business’ role in a nuanced spectrum—whether directly causing the impact, contributing to its occurrence, or being linked to the impact by business relations.
Prioritize risks to be addressed based on severity and likelihood.
3. Cease, prevent or mitigate adverse impacts
In Step 3, companies address the identified adverse impacts by employing strategic measures to cease, prevent, or mitigate these challenges within their operations, supply chains, and business relations.
For impacts caused directly by your business:
Remedy the actual impact. Develop and implement remedial activities appropriate for the identified risks and impacts, with a focus on prevention and mitigation.
Stop activities that create adverse impacts.
For impacts your business indirectly contributed to:
Cease or prevent your contribution.
Use leverage to mitigate any remaining impacts to the greatest extent possible.
For impacts your business is linked to through products or services of a business relationship:
Use leverage to influence the entity causing the adverse impact to prevent or mitigate the impact.
While undertaking risk mitigation, companies must embrace continuous improvement. Collaboration with peers, suppliers, and local stakeholders is encouraged. Disengage from a supplier or business relationship if it becomes necessary, applying responsible exit principles when such decisions become unavoidable.
4. Track implementation and results
Consistent progress is key in due diligence implementation, and Step 4 emphasizes the importance of ongoing evaluation. Periodically reviewing all activities initiated in Step 2, companies are prompted to adapt, repeat, update, or enhance processes when necessary.
Monitoring the effectiveness of the due diligence process, measuring the impact of risk assessments and mitigation activities, and actively seeking stakeholder input contribute to a dynamic and responsive approach. This step fosters a culture of continuous improvement, ensuring that the due diligence framework evolves in tandem with ever-changing legislation.
5. Communicate how impacts are addressed
Step 5 focuses on communicating the outcomes of due diligence efforts. Companies are encouraged (and in the case of some regulations, required) to disclose their due diligence process and activities, providing a comprehensive account that encompasses both progress and ongoing challenges.
Disclosure is required by all due diligence legislation, but the specific requirements may range from highly specific or prescriptive, as in the case of timber legality and conflict minerals, to more generalized, as seen in broader human rights and environmental due diligence laws.
6. Provide for, or cooperate in, remediation when appropriate
Step 6 is the remediation phase. Companies are encouraged to collaborate on providing remedies when necessary. This involves reaching out to affected parties to gauge satisfaction levels with the process and outcomes.
Establishing an effective grievance mechanism becomes paramount in this step, ensuring that companies not only address adverse impacts but also actively participate in the resolution process. Some due diligence legislation, such as the German Supply Chain Law, mandates businesses to establish grievance mechanisms. Through cooperative remediation efforts, businesses contribute to a more responsible and ethical business environment.
Due Diligence Implementation: How QIMA Can Help
QIMA assists companies in implementing due diligence in their supply chains by offering comprehensive solutions that address each step described above.
Leveraging advanced technology and a global network of skilled auditors, we conduct thorough risk assessments, evaluate compliance with regulations, and ensure adherence to ethical sourcing standards. With tailored programs, we assist you in tracking implementation, communicating transparently about your impacts, and facilitating remediation efforts when needed.
We offer:
Toolkits and Training: Develop ESG and Due Diligence strategies with QIMA's toolkits and training programs.
Supply Chain Mapping: Gain visibility beyond tier 1 suppliers using QIMA's Supplier Assessment Questionnaires for comprehensive mapping and risk identification.
Risk Assessment: Mitigate ESG risks through QIMA's Risk Dashboards, offering insights to reduce environmental, social, and governance risks.
Traceability Services: Ensure raw material authenticity with QIMA's traceability services, including PO-by-PO mapping and advanced testing.
ESG and Due Diligence Audits: Verify responsible business practices with QIMA's audits, covering environmental, chemical, and ethical considerations.
Grievance Mechanism: Implement worker-centric approaches with QIMA's grievance mechanism services, integrating surveys and worker hotlines for transparent and accountable supply chains.
Learn more about our due diligence services or read our whitepaper Mandatory Human Rights & Environmental Due Diligence: How to Get Prepared for more information on due diligence compliance.
Related Articles


